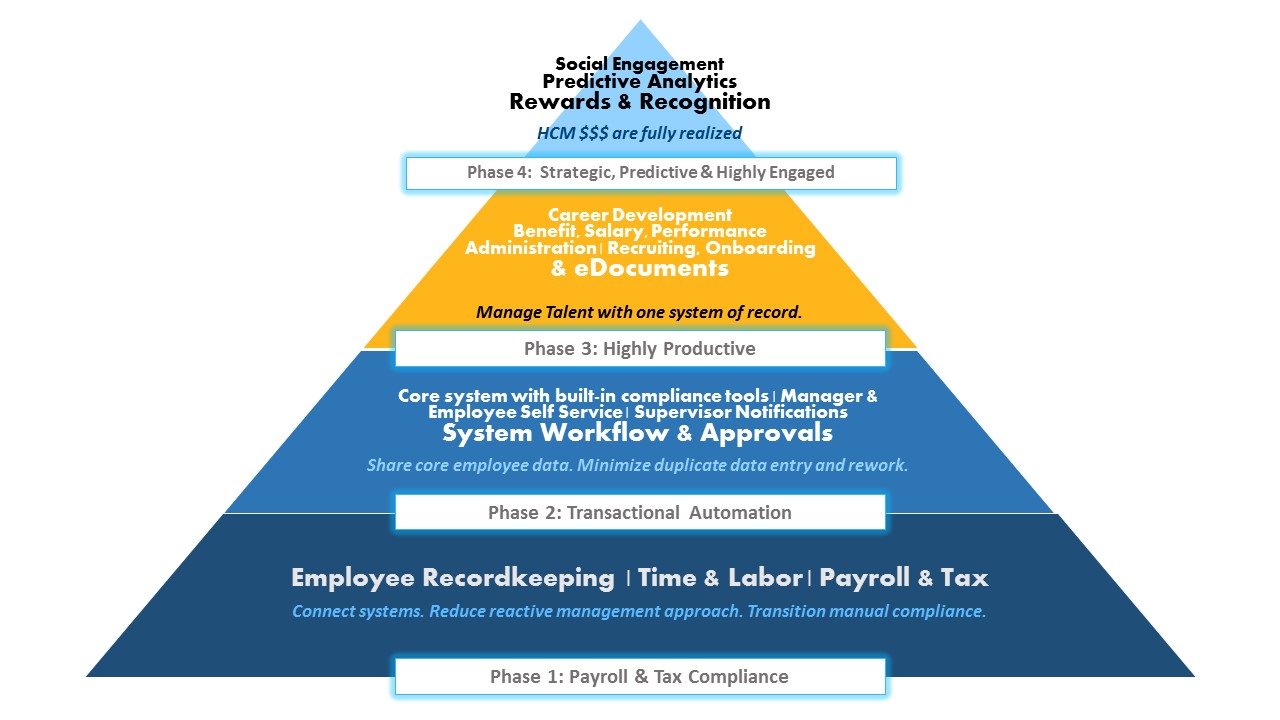
Phase 1 – Wage and hour, payroll and tax compliance requirements
Like food and shelter are to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Phase 1 HCM needs are fundamental to successful existence for any organization. An HCM implementation ensures these needs are fully met first.
Even mid-sized companies can struggle with Phase 1 needs and can find themselves in a fight for their lives. This can be due to growth spurts, mergers or acquisitions. Growth in employee counts, geographical footprint or revenue, all subject the company to governmental regulations including the Affordable Health Care Act, multi-jurisdictional taxation, and wage and hour law requirements, which strain an over-committed and growth-oriented management team. Spreadsheets, small-business payroll outsourcing and paper approvals are overwhelmed by sheer volume, inefficient procedures and duplicate processing. Information is lost, entered into systems multiple times, or otherwise inaccessible, inaccurate and/or ignored by managers.
I’ve seen first-hand how disruptive Wage and Hour or Department of Labor audits can be without the underlying recordkeeping to properly support the company; a costly event in precious time, legal fees, and fines. I have also witnessed dishonest employees and managers falsifying timesheets and payroll records literally robbing a company of payroll funds for years. Those management teams were preoccupied with growing the business and just didn’t have the proper HR systems in place to protect their company adequately.
Make no mistake that organizations with Phase 1 needs can be exciting companies with an impressive growth story, compelling products and services, and a management team engaged in fueling the rocket with talent and capital. And often those same managers are savvy enough to recognize that to continue their impressive growth story hinges on fixing these foundational HR issues.
Phase 1 of the HCM implementation is all about reduction in the number and complexity of manual paper-based payroll transactions to ensure accuracy of management reporting and compliance with governmental regulations. This means deploying HCM features like:
- A system to facilitate daily collection of time and labor (biometrics as needed) with manager oversight and approval directly fed to payroll.
- Enterprise level payroll processing with the controls needed to ensure proper federal, state, and local taxation and labor allocation broken out by the needs of the company, whether that be by location, department, project, job, and/or task. That information is ultimately reportable and fed to the general ledger so the organization has a true picture of its spending in the various areas of its business.
- HR recordkeeping practices are transitioned from small-business payroll, spreadsheets, and paper to an electronic system so this information is touched once and compliant with governmental regulations and can be managed efficiently.
Phase 2 – Improve transactional efficiency and productivity
Phase 2 is largely about workflow automation and can account for a good portion of the return on investment projected for the entire HCM project. Paper processes and duplicate work are transitioned to a vastly more efficient framework of system workflows and notifications. The organization benefits greatly by using Employee and Manager Self Service as data entry and approvals can be handled one-time and at their point of origin. Employee adoption of self-service is key to this phase and will likely require cultural reinforcement from top management.
The Phase 2 implementation delivers the benefits of HCM features like:
- Employee Self Service allows employees to help themselves via a mobile device or web browser to view or modify information about themselves, including time-off requests, timesheets, compensation, and benefits. This feature reduces the demand for HR and managers to service enquiries from employees.
- Manager Self Service empowers supervisors to manage information for their direct reports via a mobile device or web browser and to approve requests for time-off, payroll, benefit, or schedule changes online and in real-time.
- System workflows and notifications streamline approval processes that are uniquely programmed to adhere to company policy, inform all relevant decision makers and collect electronic approvals.
Phase 3 – Talent Management
Phase 3 is about Talent Management features such as Recruiting, Onboarding, Benefit Enrollment, Performance Management, Salary Administration, and Career Development. Each of these capabilities addresses a specific area of the Human Resource function with a mobile and web-based capability to engage employees and supervisors in administering this work conveniently and efficiently. Careful attention must be paid to the foundational system workflow policies to ensure that the companies underlying HR policies are respected at all times.
- Recruitment features include branded candidate mobile and web portals for job seekers, assessment and review tools for hiring managers, and system workflows to guide candidates through the process of completing job applications, screening questionnaires, interviews, and ultimately the offer process.
- Onboarding walks a newly hired employee through the hire process, collecting relevant information and signatures for hiring paperwork.
- eDocuments eliminate the paper documents and replace them with a mobile and web-based presentation and repository system that records signatures and document versioning.
- Performance management provides for talent assessments, performance reviews, and succession planning with employee, supervisors, directors, and peers all engaged in the feedback loop.
- Salary Administration distributes salary increases and bonus assignments across the entire organization respecting department, division or location budget requirements and engages the decision-makers with a multi-step approval process. Once all sign-offs are made, the system records employee and payroll changes seamlessly.
- Automate Benefit Administration using online enrollment, carrier eligibility feeds and billing reconciliation tools. Employees enroll in benefits online and changes in those enrollments are conveniently fed to carriers electronically.
Phase 4 – Social HCM and Predictive Analytics
Phase 4 is for the most committed, sophisticated, and engaged management teams. These organizations consider human capital vital and invest accordingly striving to achieve a highly-productive workforce that is highly-engaged, and this can be an elusive goal. It’s not as simple as implementing system features. An employee engagement philosophy of teamwork, collaboration, rewards, and recognition is vital along with a management commitment to transparency to the drivers of the business. And the benefits can be tremendous with productivity gains and improved employee retention. It’s a simple fact that recognition, now distributed and administered by the system, can play a big part in employee retention and productivity. As Tom Peters co-wrote in Excellence, “…the simple act of paying positive attention to people has a great deal to do with productivity.” The Social HCM acts as both a conduit for teamwork and collaboration, and it speeds the feedback loop between project stakeholders and contributors to help keep projects and people on track.
Phase 4 is focused on the following initiatives:
- Predictive Analytics provide a real-time, deep, and intuitive understanding of your organization and transparency to reveal the drivers of the business.
- Social Collaboration features foster an engaged workforce enabling employees to easily build relationships, cross-collaborate, learn, share knowledge, and ultimately improve productivity.
- Recognitions and rewards capabilities provide a framework for consistent, fair and public recognition to those deserving such accolades. Automation of badging and awards with points tracking removes the chore of reconciling points for redemption of gifts or other company rewards.
This phased methodology makes transitioning to a strategic, predictive, highly-productive, and highly-engaged workforce an orderly and controllable process. Of course, getting to the top of the pyramid requires real commitments to transparency and a philosophy that engages and rewards employees.
For organizations that aspire to be strategic, predictive, highly-productive, and highly-engaged, a modern HCM is just too compelling of a technology for those businesses to ignore.
References
McLeod, Saul. (2007/2014). Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Retrieved from http://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html
Peters, Thomas J., Waterman, Robert H., and Austin, Nancy. (1992). Excellence: In Search of Excellence and A Passion for Excellence. (pp. 94). Quality Paperback Book Club. Retrieved from https://books.google.com/books?id=scy5AAAAIAAJ&dq
 Regardless of party affiliation or politics, the first 100 days of the any new presidential administration are expected to bring change. The Trump administration is no different in that regard. He has made promises to voters and has gone as far as presenting a contract with America. With the Republican party controlling both the house and the senate, the Trump Administration has a good chance of executing on some of its promises in its first 100 days’ plan.
Regardless of party affiliation or politics, the first 100 days of the any new presidential administration are expected to bring change. The Trump administration is no different in that regard. He has made promises to voters and has gone as far as presenting a contract with America. With the Republican party controlling both the house and the senate, the Trump Administration has a good chance of executing on some of its promises in its first 100 days’ plan.
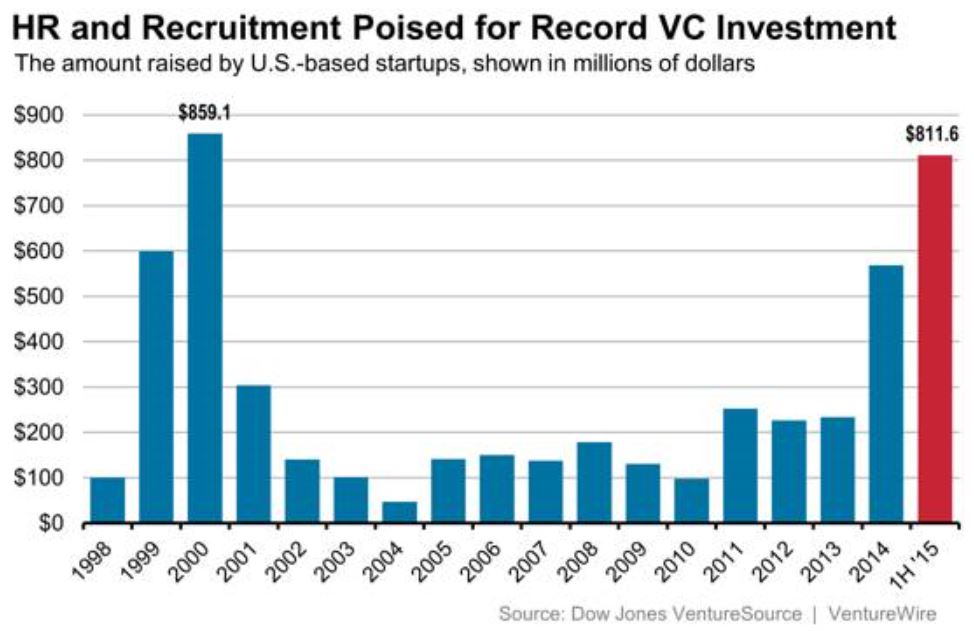 Billions of dollars invested in HR technology companies have created a handful of new and reborn one-size-fits-all HCM vendors who made a big splash on the HR scene throughout 2015 and 2016. Not to be outdone, niche HR specialist vendors have upped the ante with some very compelling niche products targeting recruiting, performance, learning, compliance, and social collaboration. Choice is always a good thing for HR departments. How does all this investment in HR technology companies change the way HR executives think about using technology within their operations?
Billions of dollars invested in HR technology companies have created a handful of new and reborn one-size-fits-all HCM vendors who made a big splash on the HR scene throughout 2015 and 2016. Not to be outdone, niche HR specialist vendors have upped the ante with some very compelling niche products targeting recruiting, performance, learning, compliance, and social collaboration. Choice is always a good thing for HR departments. How does all this investment in HR technology companies change the way HR executives think about using technology within their operations? 
 It’s really not about ageism. It is simply that a great attitude and passion to succeed trump years of experience and perfect qualifications nearly every time.
It’s really not about ageism. It is simply that a great attitude and passion to succeed trump years of experience and perfect qualifications nearly every time.